こんにちは(@t_kun_kamakiri)
本記事ではFortranの乱数生成について解説を行います。
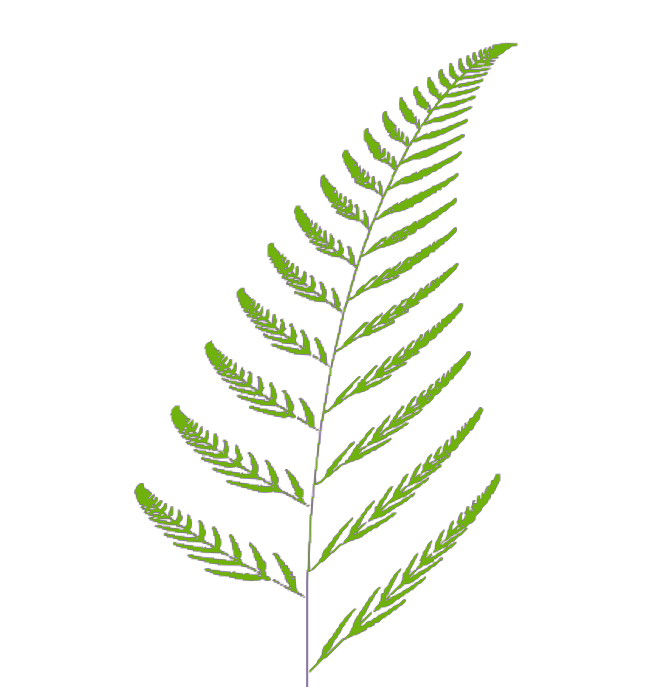
プログラミングで以下の美しい模様を再現します。
バーンズリーのシダ
Fortran + paraviewで可視化https://t.co/wshZJxkXN6 https://t.co/E0UwbhE8Tq pic.twitter.com/yxecwcSj1J
— カマキリ🐲Python頑張る昆虫 (@t_kun_kamakiri) April 20, 2022
実例を交えながら確認した方が理解しやすいし、何より楽しいと思うのでこちらに書いた「バーンズリーのシダ」のコードを例に確認していくことにします。
バーンズリーのシダ(Barnsley fern)は、イギリスの数学者マイケル・バーンズリーにちなんで名づけられたフラクタル構造を持つセイヨウメシダですね。

Fortranで遊んでみたい方にはちょうど良い題材かと思います。
コードももう少しきれいに機能ごとに各自好きなようにまとめてもらえればと思います_(._.)_
シダ生成の変換式
変換式の流れは以下となっています。
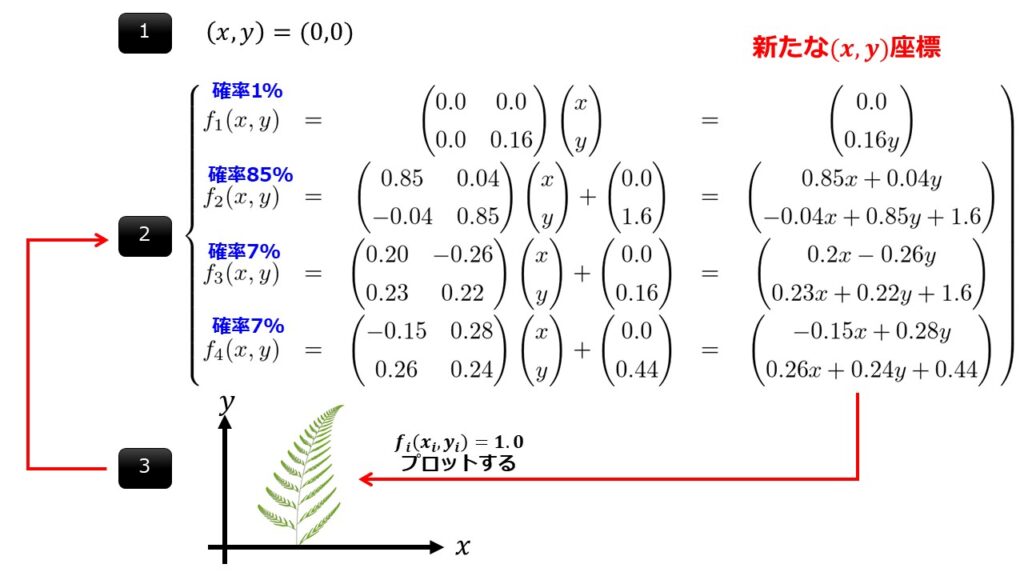
そして変換された座標をもってもう一度出現確率によって変わる座標変換式により座標変換を行います。そして、変換された座標を1.0という値を設けてラベリングします。
これを複数回(気が済むまで)繰り返していきます。
Fortranコード
Fortranコードはあえてベタ書きにした状態で残しています。
初学者がmoduleやsubroutineを使ったコードを見ると理解が難しかったりするので、最初から最後まで流れがわかるようにベタ書きにしています。
本当は機能ごとにコードを整理して汎用性を考慮した使いやすく且つ見やすいコードを目指すべきですが、ここではあまりこだわらないことにします。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 |
program main implicit none integer, parameter :: Nmax=500000, Nx=512, Ny=512 double precision, parameter :: Lx=6.d0, Ly=6.d0, dx=Lx/dble(Nx), dy=Ly/dble(Ny) complex(kind(0d0)), parameter :: uso=(0.d0,1.d0) integer :: i, j, n, m, ix, iy real(kind=8)::random_value double precision:: x, y double precision, allocatable, dimension(:) :: x_, y_ double precision, allocatable, dimension(:,:) :: f character(len=40) filename call system("mkdir data") ! 配列の割付 allocate(x_(0:Nx-1), y_(0:Ny-1)) allocate(f(0:Nx-1,0:Ny-1)) m = 0 ! x, y座標 x = 0 y = 0 do i=0, Nmax call random_seed !乱数の初期値 call random_number(random_value) ! 座標変換 if (0<= random_value .and. random_value<0.01) then x = 0.d0 y = 0.16d0*y ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 else if (0.01d0<= random_value .and. random_value<0.86d0) then x = 0.85*x + 0.04d0*y y = -0.04d0*x + 0.85d0*y +1.6d0 ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 else if(0.86d0<= random_value .and. random_value<0.93d0) then x = 0.2d0*x - 0.26d0*y y = 0.23d0*x + 0.22d0*y +1.6d0 ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 else x =-0.15d0*x + 0.28d0*y y = 0.26d0*x + 0.24d0*y +0.44d0 ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 end if end do !座標生成 do i=0,Nx-1 x_(i) = -Lx/2.d0+dx*dble(i) y_(i) = -Ly/2.d0+dy*dble(i) end do !----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- !output of movie file write(filename,"(a,i5.5,a)") "data/barsley_",int(m),".vtk" open(10,file=filename) write(10,"('# vtk DataFile Version 3.0')") write(10,"('test')") write(10,"('ASCII ')") write(10,"('DATASET STRUCTURED_GRID')") write(10,"('DIMENSIONS ',3(1x,i3))") Nx, Ny, 1 write(10,"('POINTS ',i9,' float')") Nx*Ny*1 do j=0,Ny-1 do i=0,Nx-1 write(10,"(3(f9.4,1x))") x_(i), y_(j), 0.d0 end do end do write(10,"('POINT_DATA ',i9)") Nx*Ny*1 !date input write(10,"('SCALARS julia float')") write(10,"('LOOKUP_TABLE default')") do j=0,Ny-1 do i=0,Nx-1 write(10,*) f(i,j) end do end do close(10) deallocate(x_, y_, f) end program main |
こちらのコードを実行してparaviewで可視化するときれいな植物模様ができます。

乱数の生成
乱数の生成は以下の部分です。
|
1 |
call random_number(random_value) |
これによりrandom_valueには 0から1までの実数の乱数が一様分布で出現します。
一様分布に従う乱数を使って確率に応じてif文で場合分けをして座標変換を行っています。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
! 座標変換 if (0<= random_value .and. random_value<0.01) then x = 0.d0 y = 0.16d0*y ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 else if (0.01d0<= random_value .and. random_value<0.86d0) then x = 0.85*x + 0.04d0*y y = -0.04d0*x + 0.85d0*y +1.6d0 ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 else if(0.86d0<= random_value .and. random_value<0.93d0) then x = 0.2d0*x - 0.26d0*y y = 0.23d0*x + 0.22d0*y +1.6d0 ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 else x =-0.15d0*x + 0.28d0*y y = 0.26d0*x + 0.24d0*y +0.44d0 ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 end if |
アニメーション
今回の結果を動画にしたい場合のプログラムは以下となります。
上記のプログラム同様ベタ書きしています。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 |
program main implicit none integer, parameter :: Nmax=500000, Nx=512, Ny=512 double precision, parameter :: Lx=6.d0, Ly=6.d0, dx=Lx/dble(Nx), dy=Ly/dble(Ny) complex(kind(0d0)), parameter :: uso=(0.d0,1.d0) integer :: i, j, n, m, ix, iy real(kind=8)::random_value double precision:: x, y double precision, allocatable, dimension(:) :: x_, y_ double precision, allocatable, dimension(:,:) :: f character(len=40) filename call system("mkdir data") ! 配列の割付 allocate(x_(0:Nx-1), y_(0:Ny-1)) allocate(f(0:Nx-1,0:Ny-1)) m = 0 ! x, y座標 x = 0 y = 0 !座標生成 do i=0,Nx-1 x_(i) = -Lx/2.d0+dx*dble(i) y_(i) = -Ly/2.d0+dy*dble(i) end do do m=0, Nmax call random_seed !乱数の初期値 call random_number(random_value) ! 座標変換 if (0<= random_value .and. random_value<0.01) then x = 0.d0 y = 0.16d0*y ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 else if (0.01d0<= random_value .and. random_value<0.86d0) then x = 0.85*x + 0.04d0*y y = -0.04d0*x + 0.85d0*y +1.6d0 ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 else if(0.86d0<= random_value .and. random_value<0.93d0) then x = 0.2d0*x - 0.26d0*y y = 0.23d0*x + 0.22d0*y +1.6d0 ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 else x =-0.15d0*x + 0.28d0*y y = 0.26d0*x + 0.24d0*y +0.44d0 ix = int(Nx/2 + x*Nx/10) iy = int(y * Ny /12) f(ix,iy) = 1.0d0 end if !----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- !output of movie file if ( mod(m,1000)==0 ) then write(filename,"(a,i5.5,a)") "data/barsley_",int(m),".vtk" open(10,file=filename) write(10,"('# vtk DataFile Version 3.0')") write(10,"('test')") write(10,"('ASCII ')") write(10,"('DATASET STRUCTURED_GRID')") write(10,"('DIMENSIONS ',3(1x,i3))") Nx, Ny, 1 write(10,"('POINTS ',i9,' float')") Nx*Ny*1 do j=0,Ny-1 do i=0,Nx-1 write(10,"(3(f9.4,1x))") x_(i), y_(j), 0.d0 end do end do write(10,"('POINT_DATA ',i9)") Nx*Ny*1 !date input write(10,"('SCALARS barsley float')") write(10,"('LOOKUP_TABLE default')") do j=0,Ny-1 do i=0,Nx-1 write(10,*) f(i,j) end do end do close(10) end if end do ! メモリの解放 deallocate(x_, y_, f) end program main |
アニメーションの結果はこちらです。
勉強会資料
参考書
Fortranは日本の書籍がかなり少ないのですが以下のようなサイトがあり、とても参考になります。
その他出版されている参考書を挙げておきます。
こちらの参考書は文法からちょっとした応用(偏微分方程式を解く)まで解説がありFortranを使う人にとって手元に置いておきたい参考書ですね。OpenMPによる並列計算の解説もあります。
しかし、Fortran90/95の記述のみなのでForran2003以降を学ぶにはやはり上記のサイトを参考にした方が良いでしょう。
こちらはFortranのコード集となっています。
Fortranは科学計算のためのプログラミング言語ですので数値計算の参考コードがいっぱい載っているこちらの参考書はとても勉強になります。
Fortran文法の解説はありませんが、数値計算の勉強にはとても良いです。
こちらはC言語とFortranの両方を学びながら数計算の基礎力を身に付けるための参考書です。問題演習の全てにサンプルコードがあるため本書を読みながらサンプルコードをじっくり眺めるだけでも大変力が付きます。