こんにちは(@t_kun_kamakiri)
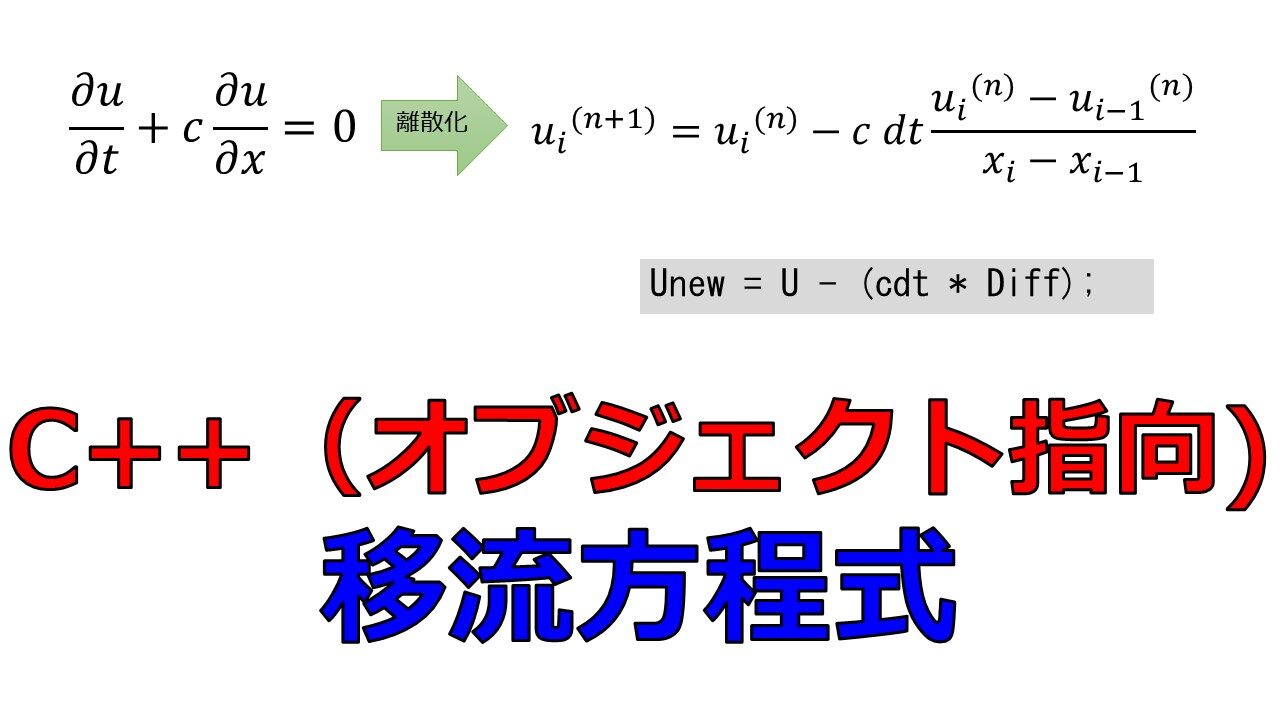
本記事ではC++を使った1次元移流方程式を題材にオブジェクト指向でのコーディングを解説します。
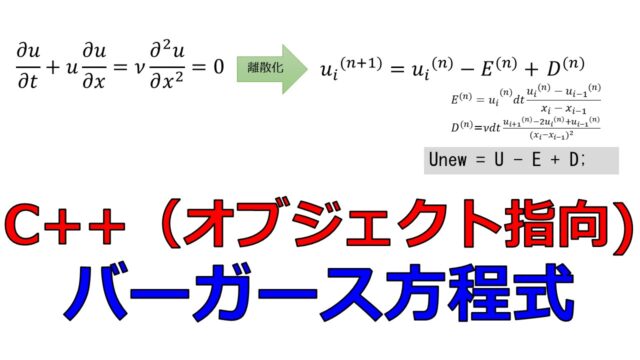
1次元の移流方程式をC++で数値計算
C++は3か月前に勉強を始めたばかりなのでコーディングスタイルの良し悪しに関してはこれからもっと磨いていかないといけないと思っています。今回はアウトプットの場として勉強したことをメモとして残しておきます。
【環境】
Microsoft Visual C++ (Visual Stido 2022)
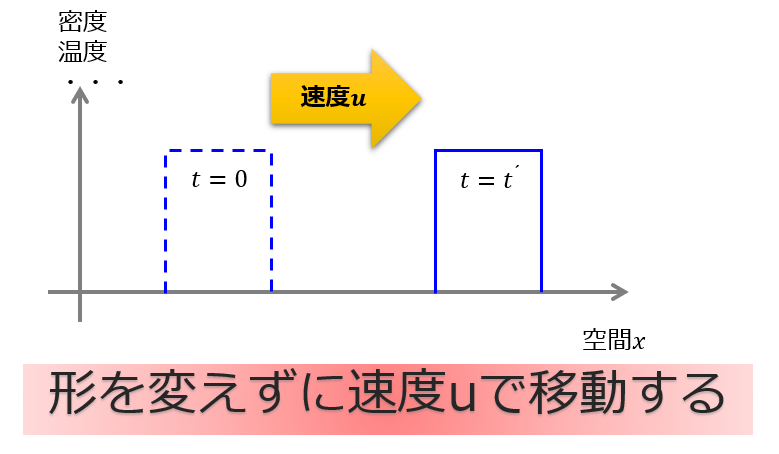
1次元の移流方程式とは何か
まずは1次元移流方程式の解説を行います。
1次元の移流方程式の一般解
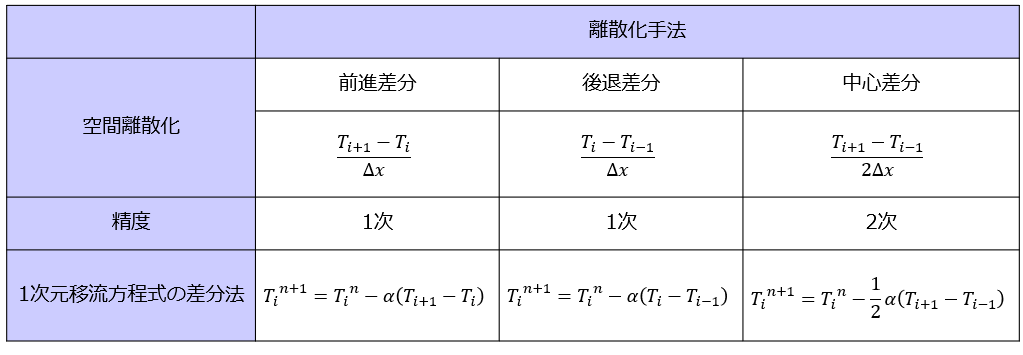
1次元の移流方程式の差分法
1次元の移流方程式の厳密解がどのような振る舞いをするのかを理解しました。
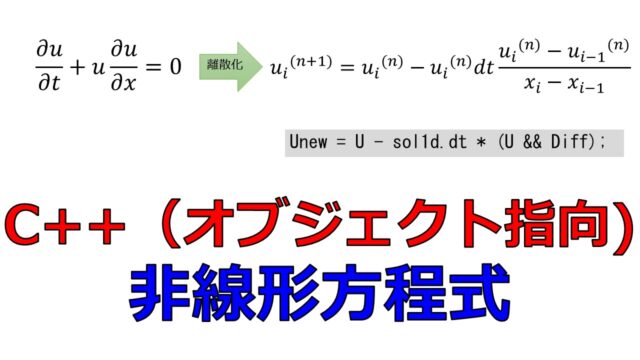
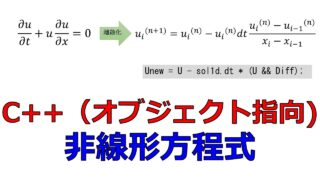
以下の3パターンの空間微分の差分法の違いによって数値計算の結果の振る舞いが変わってくることを下記の記事で確認しました。
- 前進差分で解く
- 後退差分で解く
- 中心差分で解く
全体のコード
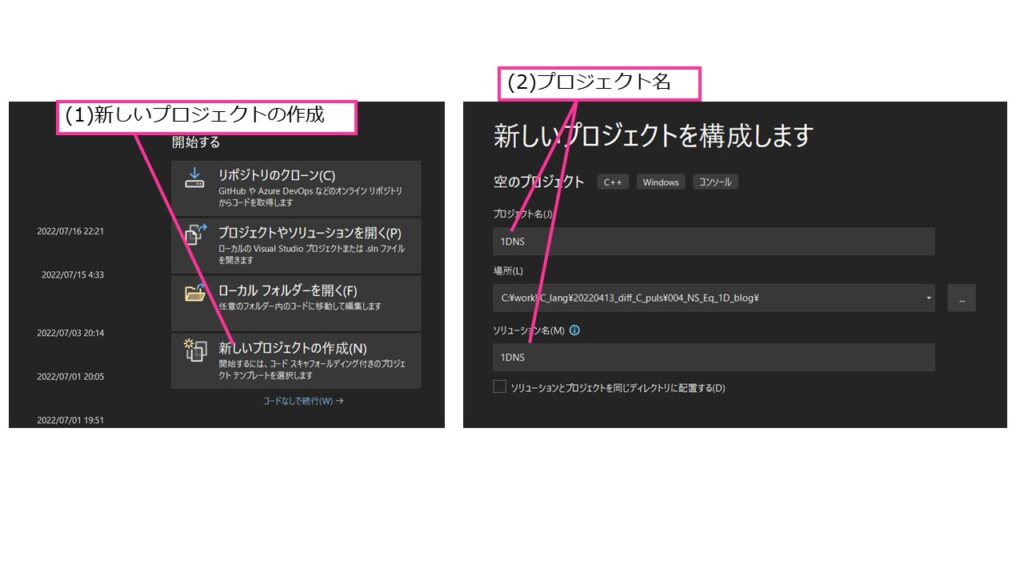
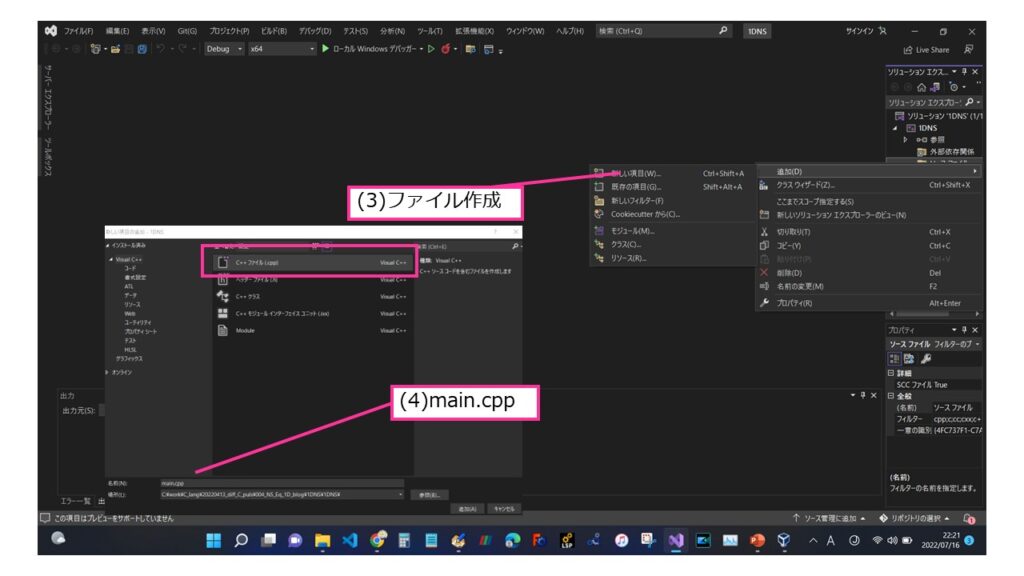
Visual Stdioでプロジェクトを作成します。


まずは全体のコードを示しておきます。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 |
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include "Mesh.h" //メッシュ設定 #include "Fields.h" //場の定義 #include "Diff1d.h" //空間微分 #include "Solution1D.h" //時間ループ #include "FileWriter.h" //ファイル出力 using namespace std; using std::vector; int main() { int Nx =100; double totallength = 2.0; Mesh mesh_(Nx, totallength);//Meshクラスのインスタンス化 // UFields(typedef vector<Fields> vectorField1d;) Fields FieldsOperations; Fields::vectorField1d U(mesh_.NumberOfNode); Fields::vectorField1d Unew(mesh_.NumberOfNode); U = FieldsOperations.passGridinfomation(U, mesh_.xpts); Unew = FieldsOperations.passGridinfomation(Unew, mesh_.xpts); //initial condition cout << "Initial :: Iteration completed, writing the final file" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < U.size(); i++) { U[i].value = 1.0; if ((U[i].x1d > 0.5) && (U[i].x1d < 1.0)) { U[i].value = 2.0; } } Unew = U; //file writer string name = "1dLinearConvec"; FileWriter filewriterObject_; filewriterObject_.write1dField(Unew, name); // solution class int ntimestep = 500; double dt = 0.001; fd1d::Diff1d diff1d; Solution1d sol1d(ntimestep, dt); for (int nt = 0; nt < sol1d.nt; nt++) { cout << "Iteration no : " << nt << endl; U= Unew; double wavespeed = 1.0; double cdt = sol1d.dt * wavespeed; Fields::vectorField1d Diff = diff1d.gradX1d(U); Unew = U - (cdt * Diff); // du/dt = c*du/dx => Unew{i} = U{i} - c*dt(u{i} - u{i-1})/dx // ノイマン条件 Unew[0].value = Unew[1].value; Unew[U.size() - 1].value = Unew[U.size() - 2].value; } //file writer string name2 = "1dLinearConvec_final"; FileWriter filewriterObject_1; filewriterObject_1.write1dField(Unew, name2); return 0; } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
#ifndef MESH_H #define MESH_H #include "Mesh.h" #include <vector> using std::vector; class Mesh { public: Mesh(); //constructor Mesh(int&, double&); //引数ありconstructor virtual ~Mesh();//deconstructor int NumberOfNode;//x分割数 double lengthx;//x方向長さ double dx1d;//分割幅 vector<double> xpts;//x座標 void discritized1dgrid(vector<double>&); //x[i]の作成 }; #endif //MESH_H |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
#include "Mesh.h" #include <iostream> Mesh::Mesh() { } Mesh::Mesh(int& n, double& txlengthx): NumberOfNode(n),//x分割数 lengthx(txlengthx),//x方向長さ xpts(NumberOfNode, 0.0)//vector(要素数, 値) { dx1d = lengthx / (NumberOfNode-1); discritized1dgrid(xpts); //add } void Mesh::discritized1dgrid(vector<double>& vec) { for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i++) //vec[0]=0なのでi=1からループする { vec[i] = vec[i - 1] + dx1d; } } Mesh::~Mesh() { } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
#ifndef FIELDS_H #define FIELDS_H #include "Mesh.h" #include <vector> using std::vector; class Fields { public: Fields();//constructor virtual ~Fields(); //deconstructor typedef vector<Fields> vectorField1d; double x1d; //x座標 double value; //Uの値 Fields::vectorField1d passGridinfomation(Fields::vectorField1d&, vector<double>&); //演算子のオーバーロード friend Fields::vectorField1d operator+(const Fields::vectorField1d&, const Fields::vectorField1d&); friend Fields::vectorField1d operator-(const Fields::vectorField1d&, const Fields::vectorField1d&); friend Fields::vectorField1d operator&&(const Fields::vectorField1d&, const Fields::vectorField1d&); friend Fields::vectorField1d operator*(const double&, const Fields::vectorField1d&); friend Fields::vectorField1d operator*(const Fields::vectorField1d&, const double&); }; #endif //FIELDS_H |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 |
#include "Fields.h" #include <iostream> Fields::Fields(): x1d(0.0), value(2.0) { } Fields::vectorField1d Fields::passGridinfomation(Fields::vectorField1d& vec, vector<double>& xpts_) { /* typedef vector<Fields> vectorField1d; double value; double x1d; */ for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) { vec[i].x1d = xpts_[i]; } return vec; } Fields::vectorField1d operator+(const Fields::vectorField1d& vecA, const Fields::vectorField1d& vecB) { Fields::vectorField1d temp = vecA; for (int i = 0; i < vecA.size(); i++) { temp[i].value += vecB[i].value; } return temp; } Fields::vectorField1d operator-(const Fields::vectorField1d& vecA, const Fields::vectorField1d& vecB) { Fields::vectorField1d temp = vecA; for (int i = 0; i < vecA.size(); i++) { temp[i].value -= vecB[i].value; } return temp; } Fields::vectorField1d operator&&(const Fields::vectorField1d& vecA, const Fields::vectorField1d& vecB) { Fields::vectorField1d temp = vecA; for (int i = 0; i < vecA.size(); i++) { temp[i].value *= vecB[i].value; } return temp; } Fields::vectorField1d operator*(const double& dbvalue, const Fields::vectorField1d& vecB) { Fields::vectorField1d temp = vecB; for (int i = 0; i < vecB.size(); i++) { temp[i].value = dbvalue * vecB[i].value; } return temp; } Fields::vectorField1d operator*(const Fields::vectorField1d& vecB, const double& dbvalue) { Fields::vectorField1d temp = vecB; for (int i = 0; i < vecB.size(); i++) { temp[i].value = dbvalue * vecB[i].value; } return temp; } Fields::~Fields() { } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
#ifndef DIFF1D_H #define DIFF1D_H #include "Mesh.h" #include <vector> #include"Fields.h" using std::vector; namespace fd1d { // U U U U //*-----*----*----* // i-1 i class Diff1d { public: Diff1d(); Fields::vectorField1d gradX1d(Fields::vectorField1d&); virtual ~Diff1d(); }; } #endif //FIELDS_H |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
#include "Diff1d.h" #include <iostream> fd1d::Diff1d::Diff1d() { } Fields::vectorField1d fd1d::Diff1d::gradX1d(Fields::vectorField1d& vec) { Fields::vectorField1d temp = vec; for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i++) { temp[i].value = (vec[i].value - vec[i - 1].value) / (vec[i].x1d - vec[i - 1].x1d); } return temp; } fd1d::Diff1d::~Diff1d() { } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
#ifndef SOLUTION_H #define SOLUTION_H class Solution1d { public: Solution1d(int&, double&); // constructor virtual ~Solution1d(); //deconstructor int nt; //ステップ数 double dt; //時間刻み幅 }; #endif |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
#include <iostream> #include "Solution1D.h" Solution1d::Solution1d(int& nt_, double& dt_) : nt(nt_), dt(dt_) { std::cout << "Solution1d()" << std::endl; } Solution1d::~Solution1d() { } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
#ifndef FILEWRITWE_H #define FILEWRITWE_H #include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <sstream> #include <fstream> //ファイルの書き込みに必要 #include "Fields.h" using namespace std; using std::vector; using std::string; class FileWriter { public: FileWriter();//constructor virtual ~FileWriter(); //destructor void write1dField(Fields::vectorField1d&, string&); }; #endif |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
#include "FileWriter.h" #include <iostream> FileWriter::FileWriter() { } void FileWriter::write1dField(Fields::vectorField1d& vec, string& name_) { string myfileType = ".dat"; //拡張子 string path = "C:\\work\\C_lang\\20220413_diff_C_puls\\\004_NS_Eq_1D_blog\\1DNS\\1DNS\\"; //絶対パス string pathName = path.append(name_).append(myfileType); //"myOutput;" + ".dat" => "myOutput.dat" std::cout << "pathName = " << pathName << " : pathName.size() = " << pathName.size() << std::endl; FILE* outfile; fopen_s(&outfile, pathName.c_str(), "w+t"); //https://www.paveway.info/entry/2018/12/25/cpp_std_string_char std::cout << "outfile = " << &outfile << std::endl; for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) { double xpos = vec[i].x1d; double uvel = vec[i].value; if (outfile) { fprintf(outfile, "%5.8lf\t%5.8lf\n", xpos, uvel); } } fclose(outfile); } FileWriter::~FileWriter() { } |